Definition of Process:
According to the Oxford Dictionary, a process is defined as a series of actions taken in a specific order to achieve a particular result. The ISO 9000 standard defines a process as a set of interrelated or interacting activities that transform inputs into outputs.
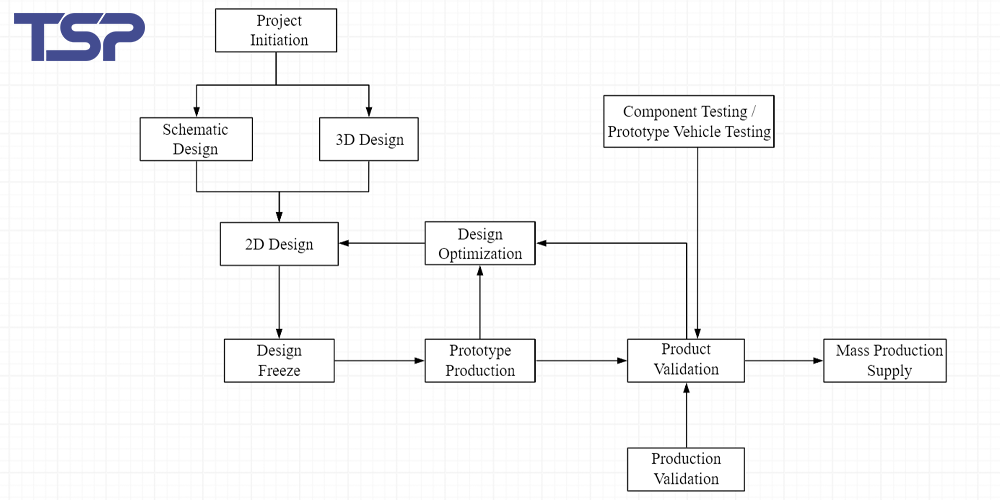

1. Wire Harness Product Development Process
Understanding the wire harness product development process is essential for managing the design and production from a system-wide perspective. A clear product development flow helps coordinate each phase of development and ensures efficiency, quality, and traceability.
In general, the development of wire harnesses involves several synchronized steps, including:
Vehicle schematic design
3D electrical layout planning
Wire routing and harness design
Material selection
Prototype building and testing
Design validation and improvement
Each phase includes sub-processes, documentation, and feedback loops to support continuous improvement. The integration between system design and physical layout is particularly critical.
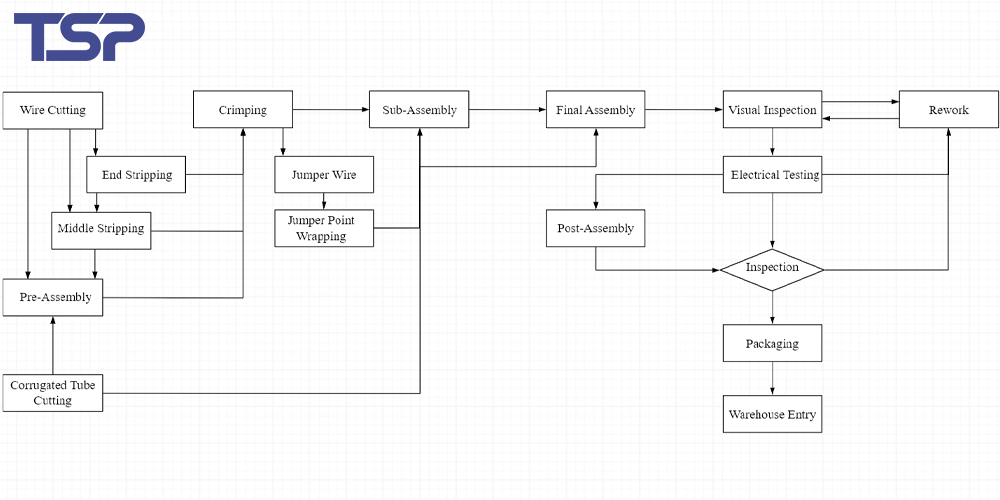
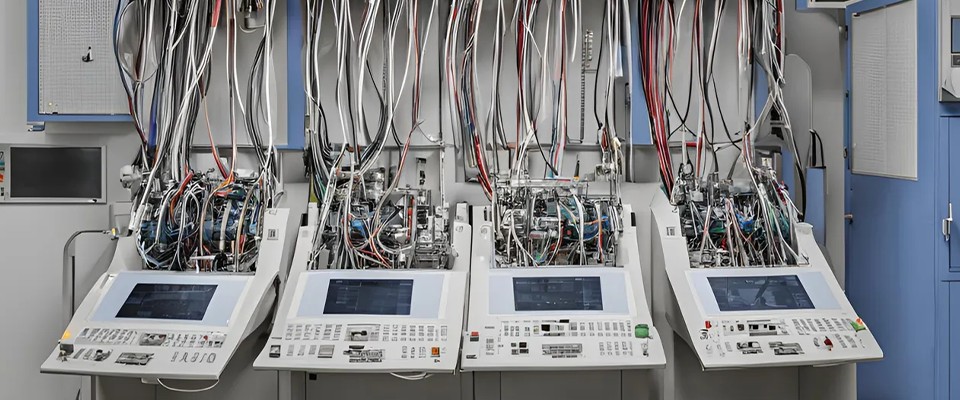
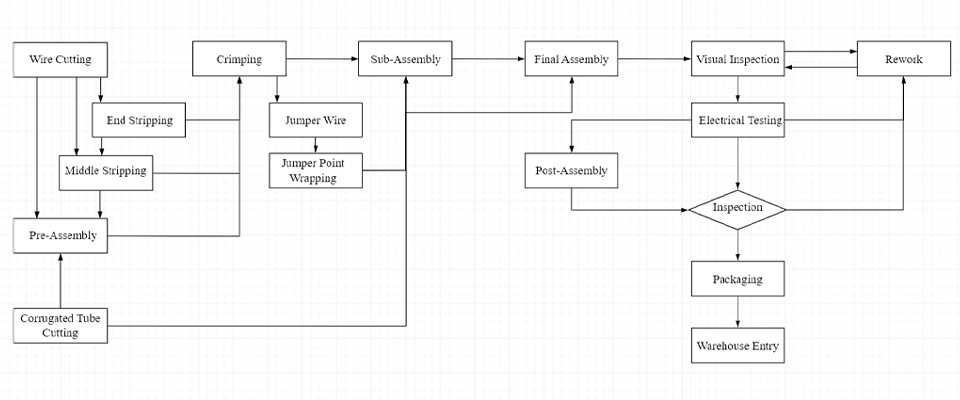
2. Wire Harness Manufacturing Process
Whether in OEM (original equipment manufacturers) or component suppliers, understanding the wire harness manufacturing process is fundamental for engineers and technicians. While process names may differ slightly between companies, the core steps typically include:
Incoming material inspection and storage
Wire cutting and stripping (Cutting Process)
Terminal crimping (Crimping Process)
Pre-assembly (Sub-assembly Process)
Final assembly (Main Assembly Process)
Product inspection (Appearance, Dimensions, Electrical Testing, etc.)
Packaging and labeling
Each step requires detailed work instructions, inspection standards, and supporting documentation to ensure consistent quality and production traceability.

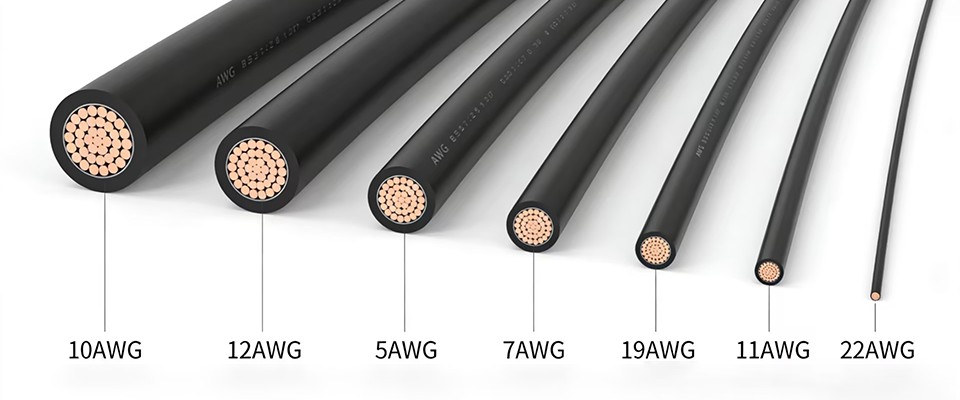
2.1 Wire Cutting (Cutting Process)
Definition:
Wire cutting involves cutting wires to specified lengths, stripping insulation, and bundling wires based on design and process documentation.
Process Steps:
Prepare materials
Set up and adjust equipment
First article inspection (measure wire length and stripping accuracy)
Mass production with in-process inspection
Organize wires for the next station
Quality Checkpoints:
Wire length tolerance
Full and partial stripping length
Opening length accuracy
Documentation such as the Wire Cutting and Crimping Table guides this process.

2.2 Terminal Crimping (Crimping Process)
Definition:
Crimping is the process of attaching terminals to wire ends using mechanical compression.
Process Steps:
Material preparation
Equipment setup
First article production
First piece inspection (crimp height, width using micrometers)
Batch production with 100% in-line inspection
Parts staging for next process
Inspection Requirements:
R-radius presence
Visible wire and insulation lengths within tolerance
No damage to core or insulation
Crimp twist and deformation within limits

2.3 Pre-Assembly (Sub-Assembly Process)
Definition:
Pre-assembly involves assembling semi-finished wires with components like sleeves, tubes, and rubber parts to form new subassemblies.
Key Technique:
Insert → Listen → Pull-back (used for confirming secure connector insertion)
Inspection:
Self-check during the process using the “Insert-Listen-Pull” method and ensuring proper locking features are in place.
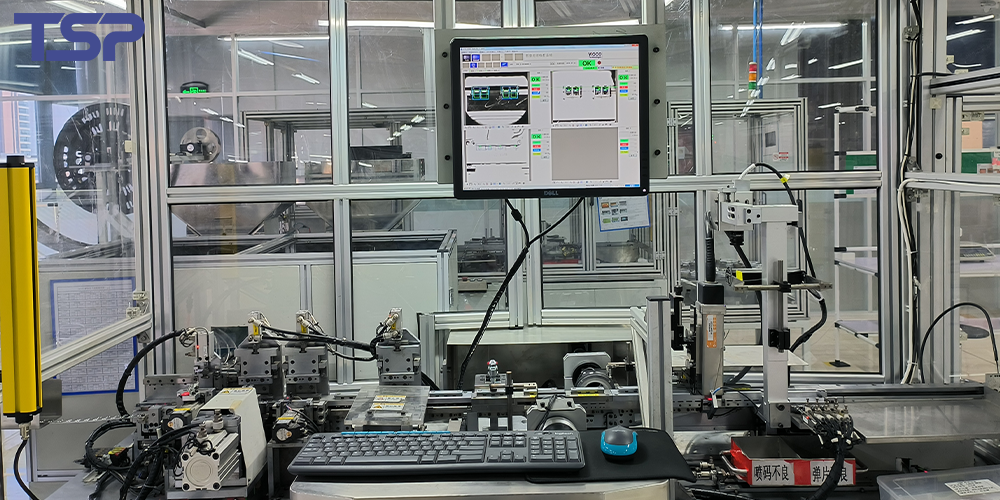

2.4 Final Assembly (Main Assembly Process)
Definition:
Final assembly combines all processed wires, terminals, and subassemblies into complete wire harnesses. It includes bundling wires using tape or cable ties based on the final layout and drawing.
2.5 Quality Inspection Process
Inspection Types:
Visual Inspection (Appearance and Accessories)
Dimensional Inspection
100% Electrical Testing
Relay and Function Testing
Image-Based Inspection (for complex assemblies like fuse boxes)
Electrical Testing:
Every wire harness must undergo 100% electrical continuity and short-circuit testing.
Function Testing:
Ensures relays function properly, fuse locations are accurate, and required torque on bolt-in fuse holders is confirmed.
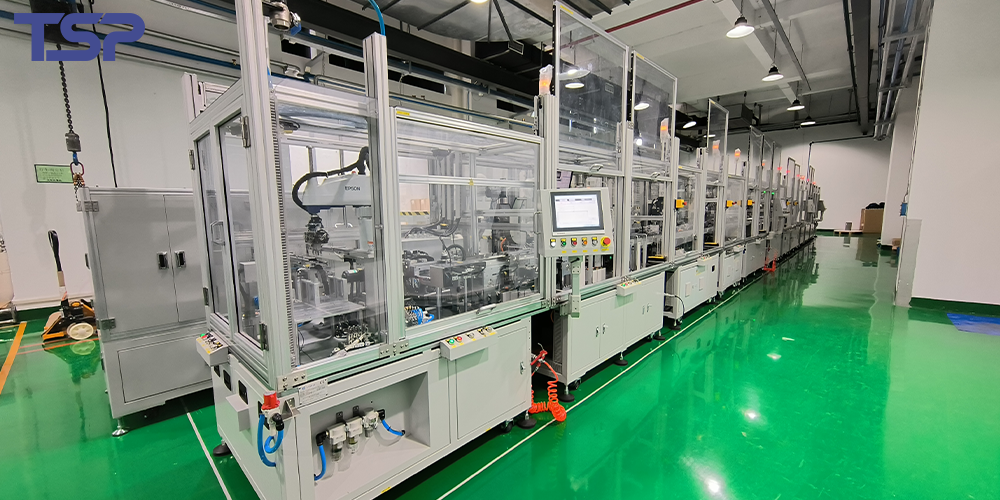

2.6 Packaging Process
Definition:
Packaging involves organizing and boxing finished wire harnesses for delivery or storage.
Process Steps:
Open and prepare carton
Tie harnesses with nylon ropes
Arrange products in box
Seal with tape
Attach labels (QC passed, serial numbers)
Apply packing tape
Send to warehouse

Final Thoughts
Mastering the wire harness product development and manufacturing process is essential for achieving high quality, cost-effective production, and on-time delivery. From concept to final inspection, each step is interconnected and must be carefully controlled to meet modern industry standards.

To read more: TSP Shanghai Achieves 1000KW Solar Power Milestone