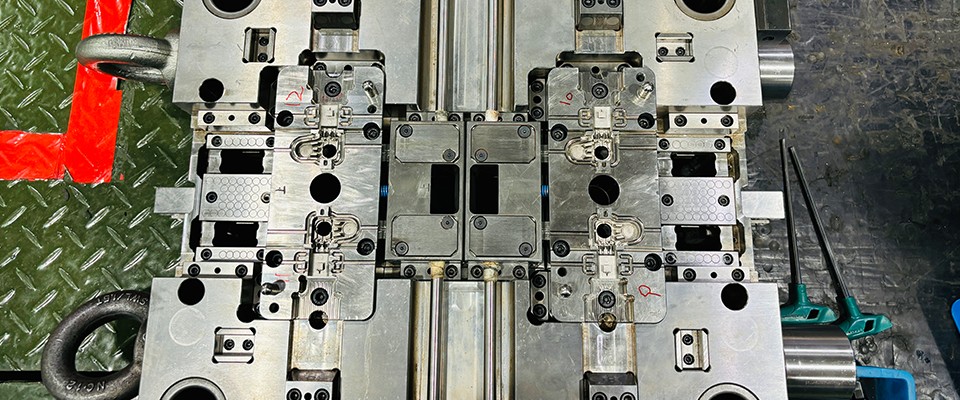
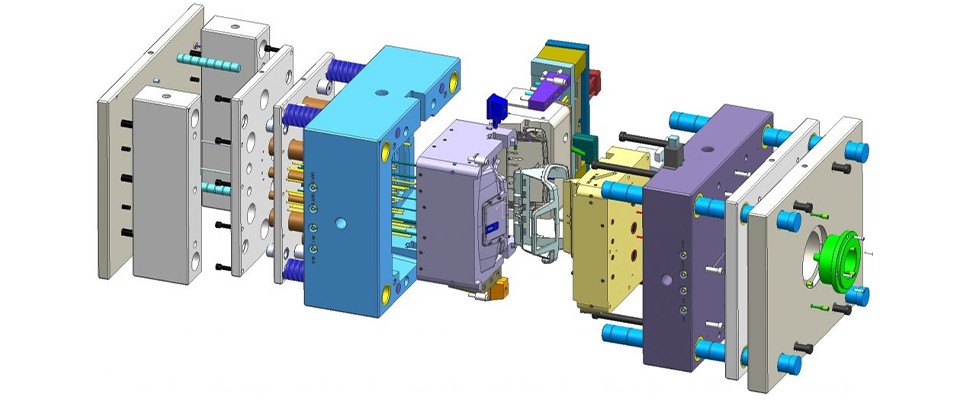
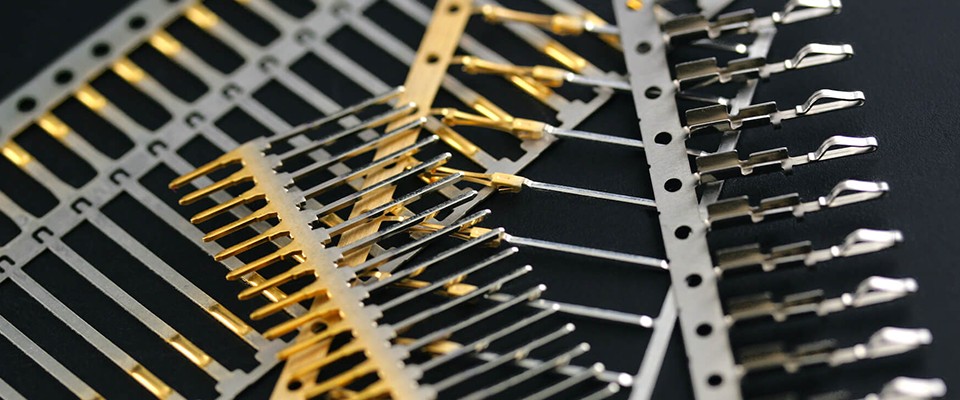
Precision mold accuracy plays a critical role in industries such as connectors, wiring harness components, medical devices, and electronic parts manufacturing. Even minor dimensional deviations can lead to assembly issues, performance instability, or increased rejection rates.
So, what are the common factors affecting precision mold accuracy?
Based on industry best practices and high-performing manufacturing cases, mold accuracy is determined by a combination of material selection, mold design, machining precision, molding process control, and production environment.
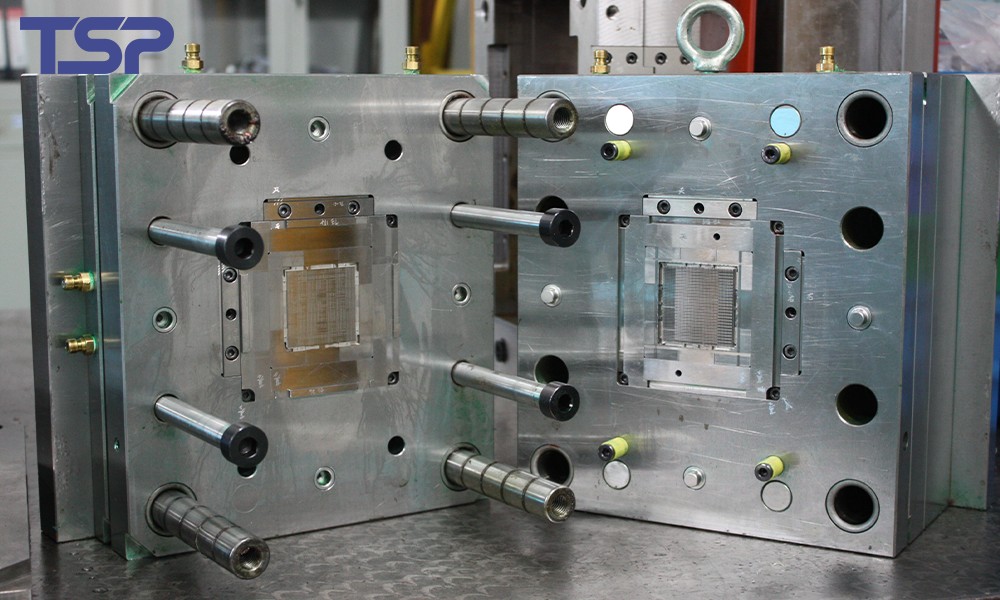
1. Material Selection: The Foundation of Mold Accuracy
Mold Steel Quality and Stability
High-precision molds require premium-grade mold steels with:
Stable chemical composition
Uniform heat treatment
Low internal stress
Poor-quality steel or improper heat treatment can cause deformation during machining or long-term production, directly reducing mold accuracy.
Plastic Material Shrinkage Characteristics
Different plastic materials exhibit different:
Shrinkage rates
Crystallization behavior
Thermal expansion properties
If these characteristics are not fully considered during mold design, final part dimensions may deviate even when mold machining accuracy is high.
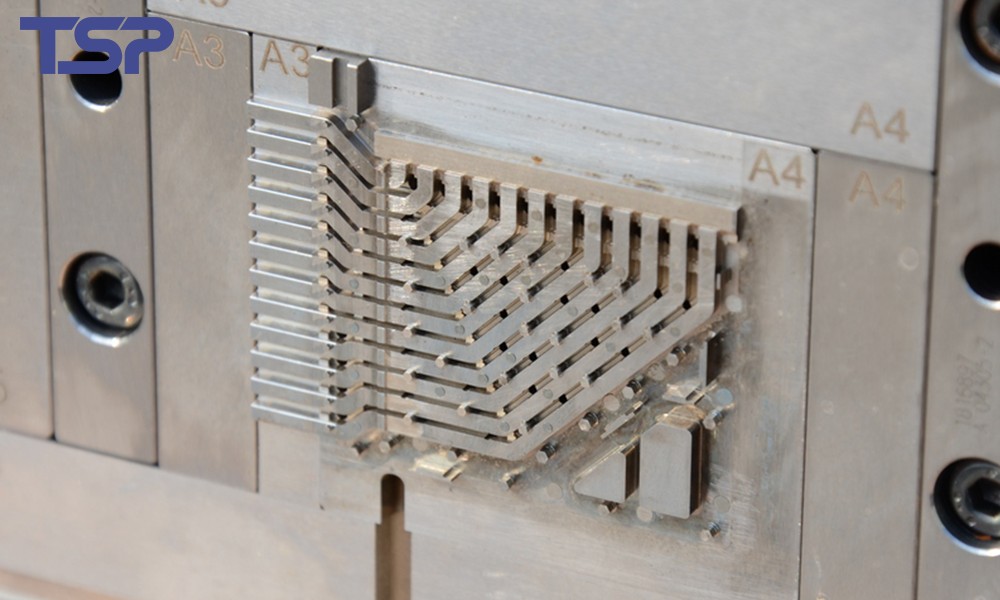

2. Mold Design Factors: Defining the Accuracy Limit
Structural Design Rationality
Precision mold accuracy depends heavily on:
Gate location and runner design
Uniform cooling system layout
Effective venting structures
Unreasonable mold design often leads to uneven filling, internal stress concentration, warpage, or dimensional instability.
Tolerance Allocation and Assembly Fit
In precision molds, each component’s tolerance directly affects overall performance. Scientific tolerance allocation ensures stable assembly and long-term accuracy during high-volume production.
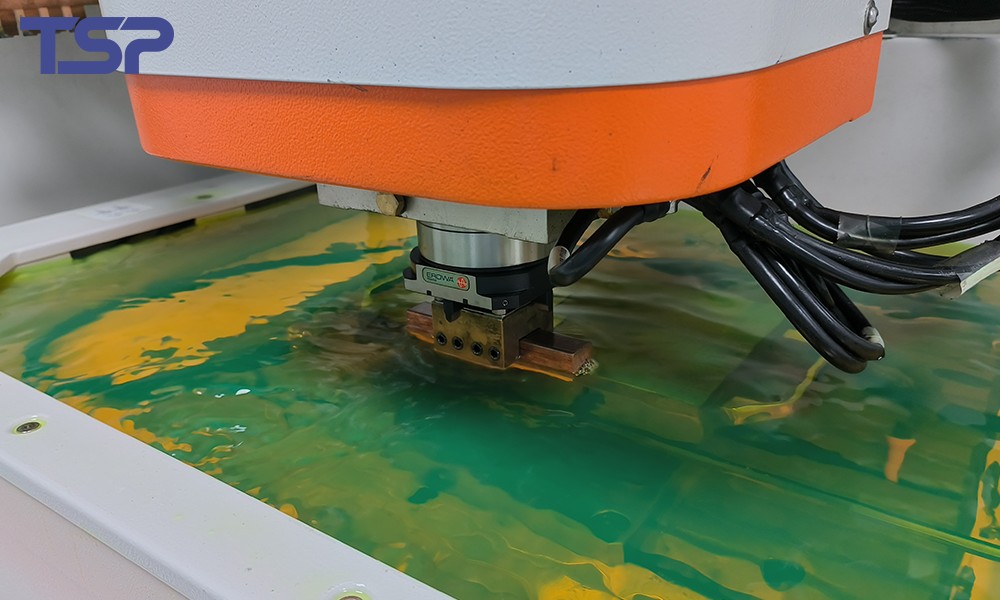

3. Mold Machining Precision: Turning Design into Reality
Machining Equipment and Technology
High-accuracy molds rely on:
Advanced CNC machining
Precision grinding
EDM and fine finishing processes
The repeatability and stability of machining equipment directly influence dimensional consistency between mold components.
Process Control During Machining
Precision mold manufacturing requires strict control of:
Tool wear
Thermal deformation
Multi-stage machining and stress relief
Experienced manufacturers focus on these details to maintain micron-level accuracy.
4. Injection Molding Process Parameters: Ensuring Accuracy Repeatability
Even a highly precise mold cannot guarantee accurate products without proper molding process control.
Key process parameters include:
Injection pressure and speed
Mold temperature control
Holding pressure and cooling time
Precision molds typically operate within narrow process windows, requiring experienced technicians and stable molding systems.
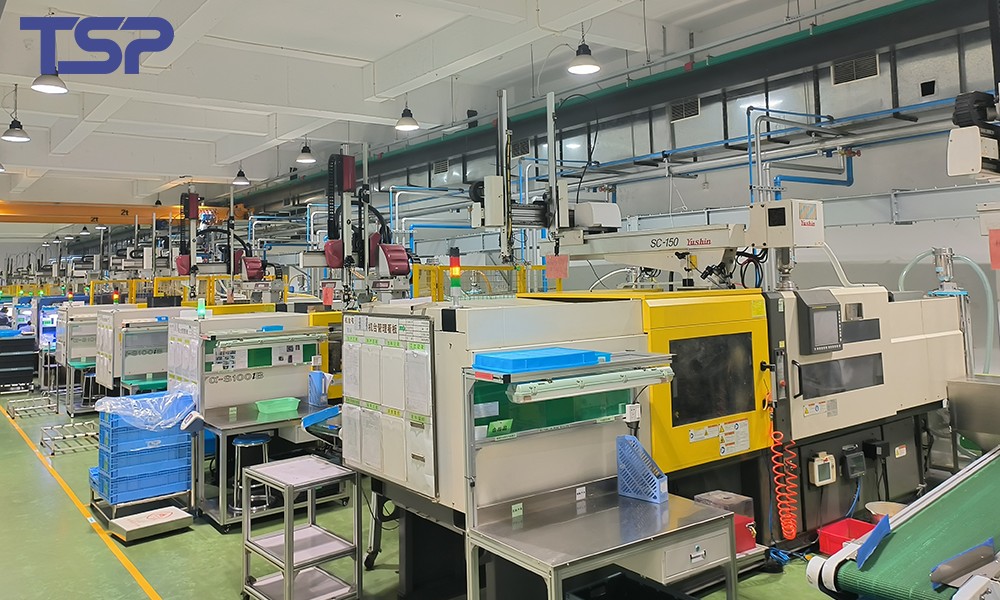

5. Equipment and Production Environment
Injection Molding Machine Stability
High-precision molding requires machines with:
High repeatability
Stable pressure control
Accurate temperature regulation
Equipment fluctuations can directly cause dimensional variation in molded parts.
Environmental Conditions
Temperature and humidity changes in the production environment can subtly affect material behavior, especially during long-term mass production.
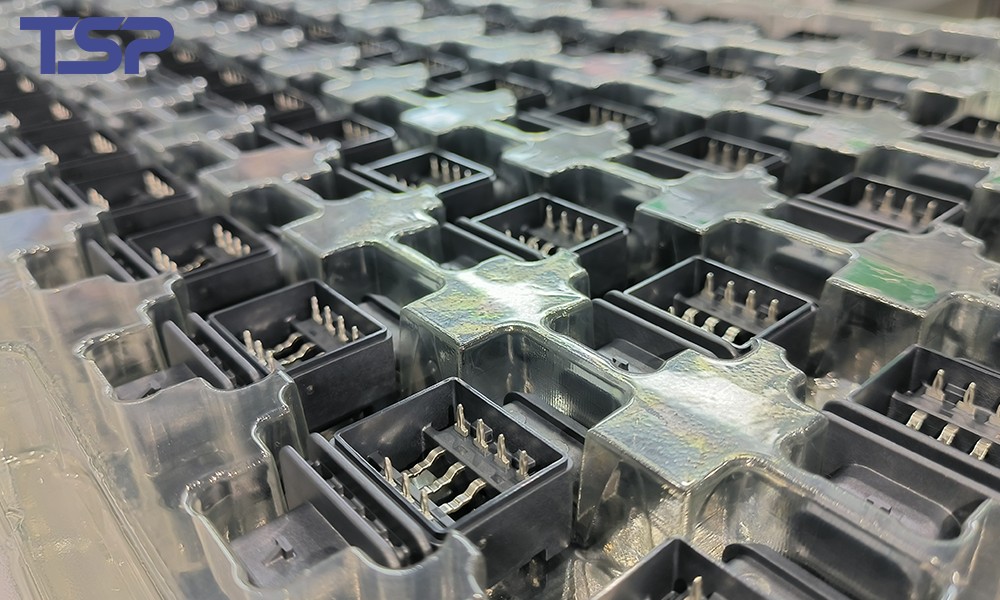

6. Why Choosing an Experienced Precision Mold Manufacturer Matters
Precision mold accuracy is never determined by a single factor. It is the result of a complete manufacturing system, including design expertise, machining capability, process control, and quality management.
Professional manufacturers like tsp.cn focus on:
Customized mold design based on product application
Stable machining and quality control processes
Consistent accuracy across mass production cycles
This is particularly critical for high-precision components such as connectors and wiring harness parts, where reliability and dimensional consistency are essential.