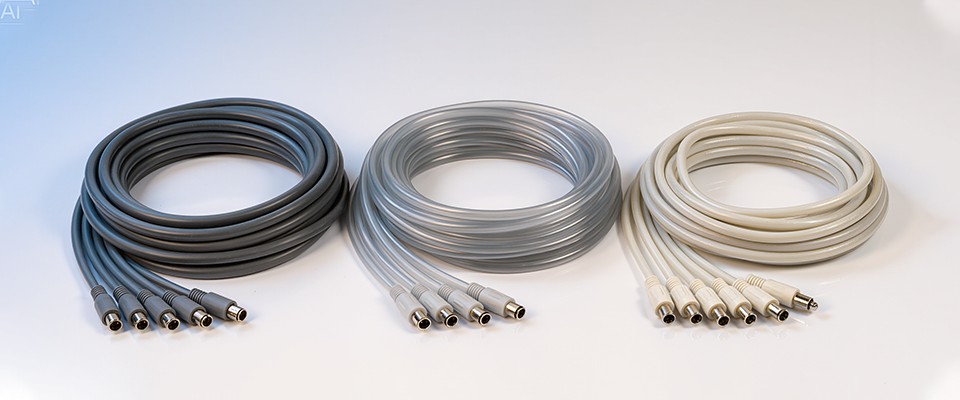
When it comes to medical-grade cables, choosing the right material is not just about performance—it’s about safety, flexibility, and durability. Among the most common materials used are PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane), and Silicone. Each has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific medical environments. Let’s take a closer look at their differences and ideal applications.
1. PVC – The Reliable and Cost-Effective Choice
PVC is one of the most widely used materials in the medical cable industry.
Advantages:
Affordable and easy to process
Excellent insulation and chemical resistance
Can be made flexible with the right formulation
Applications:
PVC cables are commonly used in disposable medical devices, patient monitoring systems, and diagnostic equipment, where cost efficiency and reliability matter most.
Drawbacks:
However, PVC can become stiff over time and may not perform well under extreme temperatures or repeated sterilization.

2. TPU – The Balance Between Strength and Flexibility
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) has become increasingly popular in modern medical applications.
Advantages:
Superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength
Excellent flexibility even in cold conditions
Resistant to oils, chemicals, and frequent cleaning
Applications:
TPU is ideal for wearable medical devices, catheter tubing, and handheld medical tools, especially when cables need to bend repeatedly without damage.
Drawbacks:
TPU tends to be more expensive than PVC and requires precise temperature control during manufacturing.

3. Silicone – The Premium Choice for Biocompatibility
Silicone is often the go-to material for high-end medical applications that require extreme flexibility and long-term contact with the human body.
Advantages:
Highly biocompatible and non-reactive
Stays soft and flexible over time
Resistant to heat, UV, and sterilization processes
Applications:
Silicone cables are commonly used in surgical instruments, implantable devices, and advanced diagnostic equipment, where comfort and reliability are critical.
Drawbacks:
Silicone is more expensive and has lower mechanical strength compared to TPU, so it’s not ideal for heavy-duty or high-tension applications.
4. Choosing the Right Material for Your Medical Device
Selecting the right wire material depends on your specific application requirements:
| Requirement | Best Option | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Low cost, general use | PVC | Affordable and reliable |
| Repeated bending, strong surface | TPU | Durable and flexible |
| Direct skin or tissue contact | Silicone | Biocompatible and soft |
If your device needs smooth flexibility and resistance to cleaning chemicals, TPU is a great balance. For premium-grade applications where biocompatibility is critical, silicone is the top choice.
In the evolving medical industry, wire material selection is becoming more critical than ever. Choosing the right one can impact not just product performance, but also patient safety and device longevity.
At TSP, we specialize in manufacturing custom medical-grade cables using PVC, TPU, and Silicone materials. Our design and engineering team ensures every cable meets international medical standards while remaining lightweight, durable, and cost-efficient.

To read more: TSP Shanghai Achieves 1000KW Solar Power Milestone