Medical devices play a crucial role in safeguarding human health. The accuracy and safety of these devices are essential, and one key factor behind their success is the manufacturing of medical molds. The precision and quality of the molds directly impact the final product, making molds an indispensable part of the medical device manufacturing process. Furthermore, molds allow for standardized and mass production, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
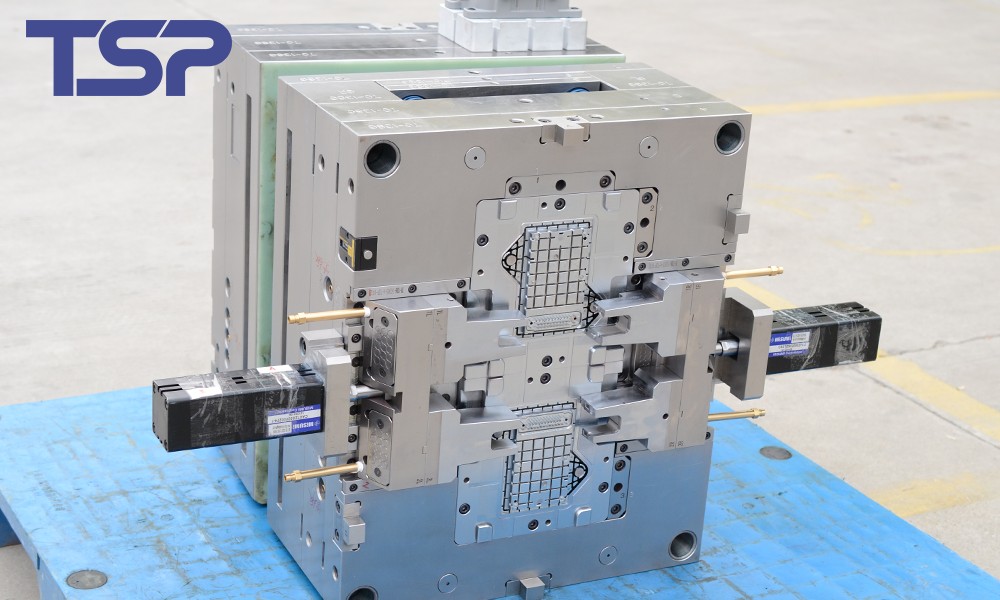
What is Precision Molding?
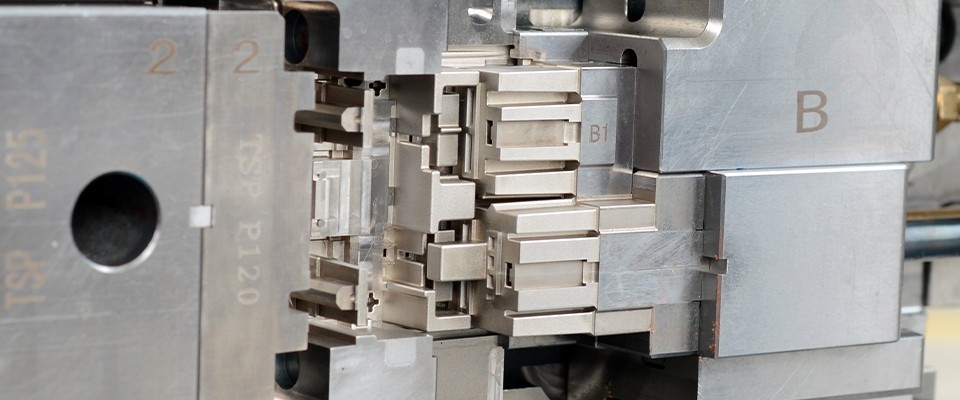
Precision molding refers to the tools used in shaping, punching, or other manufacturing processes that directly act on raw materials (typically metal or plastic). Precision molds are made through CNC machining and are designed to create highly accurate parts that meet stringent specifications.
Key Characteristics of Precision Molds:
High Precision: Precision molds can achieve accuracy down to sub-micron levels. The accuracy of the mold depends largely on the machining techniques and the physical properties of the materials used.
High Repeatability: Precision molds offer excellent consistency, ensuring that each finished product is identical in accuracy and quality when processed under the same conditions.
Long Lifespan: Well-designed precision molds are durable and can last for many years without significant wear or damage, which reduces long-term production costs.
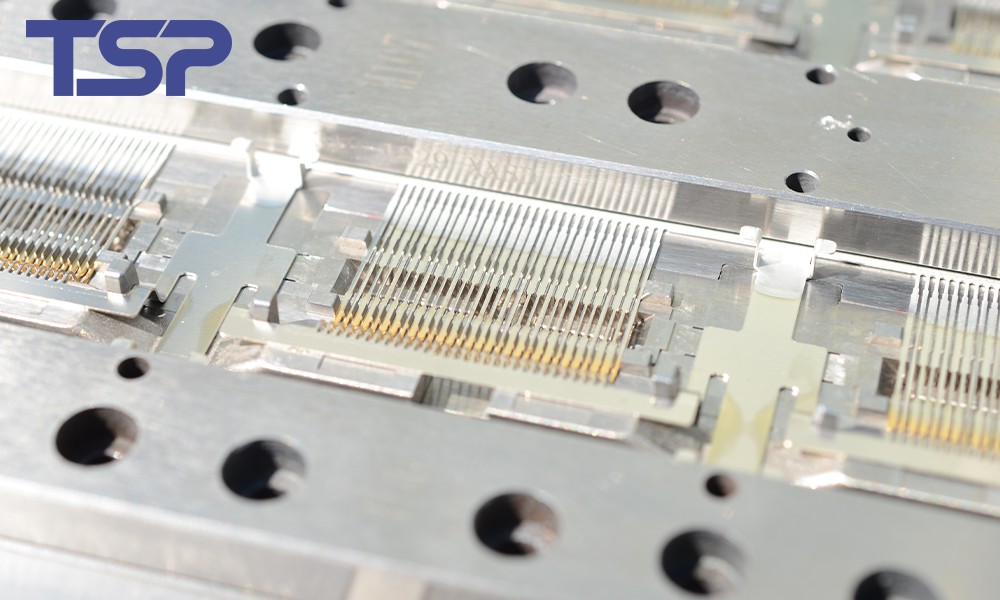
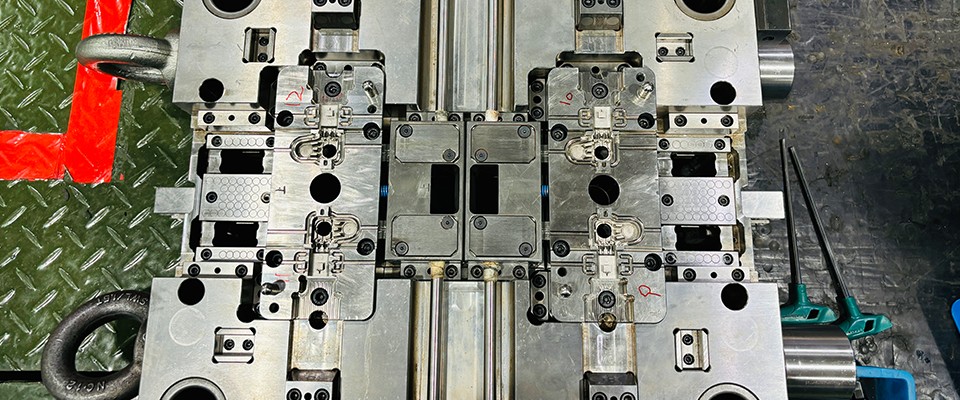
Types of Medical Device Molds
Medical device molds vary widely, ranging from single-use syringes and IV sets to complex surgical instruments, endoscopes, and parts for advanced medical imaging equipment. The molds used are designed to meet the specific requirements of these devices. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
1. Injection Molds
Injection molds are widely used in the production of plastic-based medical devices. Through an injection molding machine, molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity. Once cooled and solidified, it forms the desired medical device parts, such as syringes, catheters, and test tubes. These molds need precise control over factors like temperature, pressure, and time to ensure accuracy and quality.
Materials Used: High-strength, heat-resistant alloys or aluminum alloys are commonly used to withstand high-pressure environments.
2. Cutting Molds
Cutting molds are primarily used for the manufacturing of surgical instruments like scalpels, scissors, and forceps. These molds require high precision to ensure that the instruments meet the necessary standards for medical procedures.
Materials Used: Premium tool steels or stainless steel to ensure durability and resistance to wear.
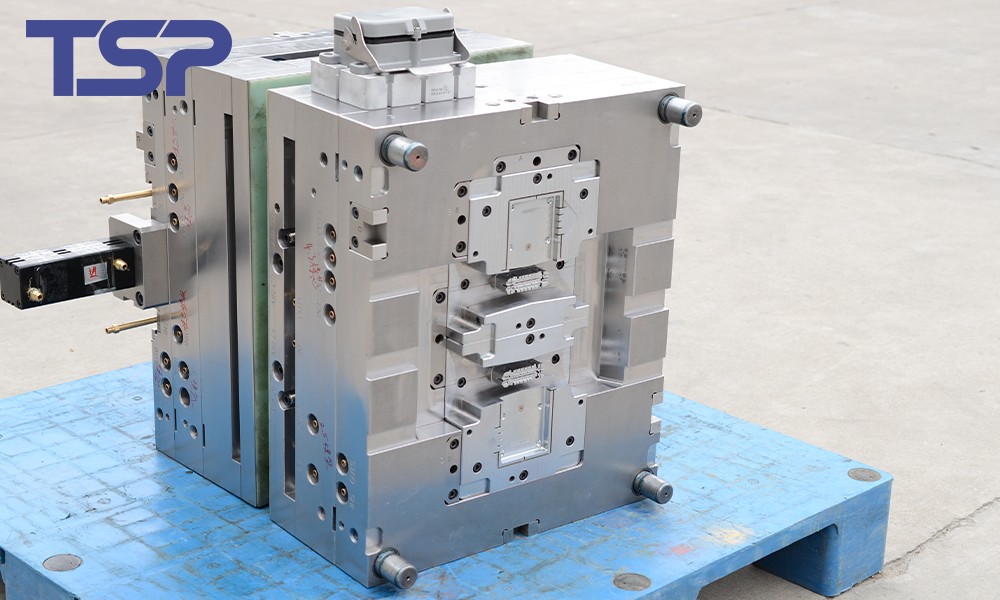

3. Forming Molds
Forming molds are used in the production of medical products such as medical-grade tubing and orthopedic splints. These molds require high precision to meet medical standards and provide the necessary functionality.
Materials Used: High-strength materials like polyimides and carbon fiber are often used for their durability and heat resistance.
4. Hot Press Molds
Hot press molds use heat and pressure to shape materials into the required form. They are ideal for producing medical device parts that require specific shapes and strength. There are three types based on material overflow: overflow, semi-overflow, and non-overflow.
5. Specialized Molds
These molds are used for performance testing, like SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) phantoms and CT dose measurement phantoms, which simulate real-life conditions for evaluating the performance of medical devices.
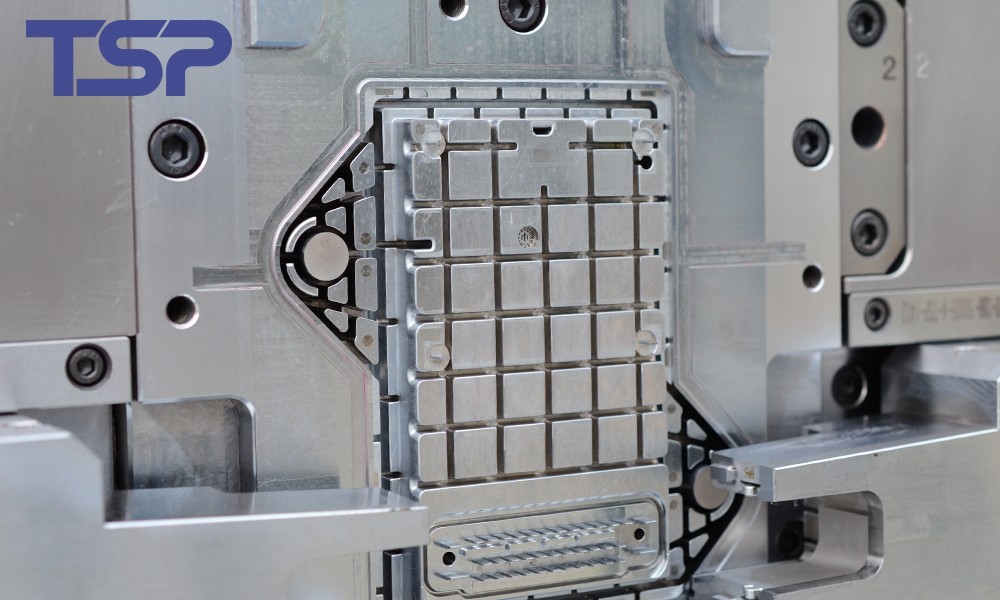
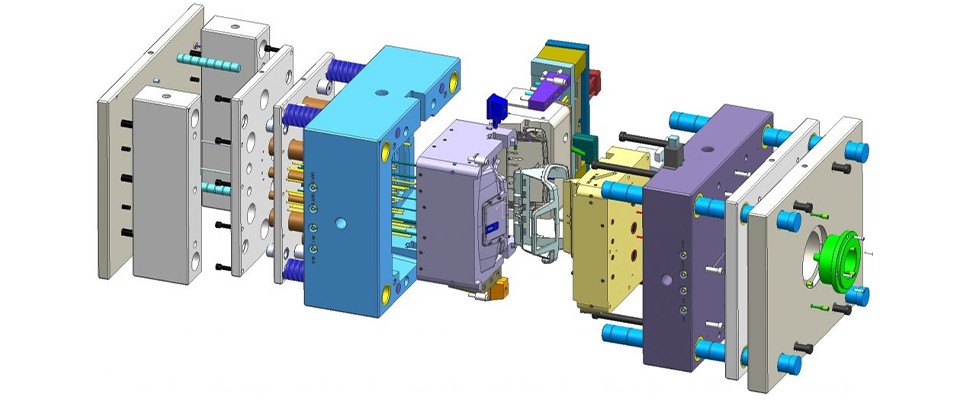
Mold Manufacturing Techniques
1. CNC Machining
CNC machining is a high-precision method used to create molds. This technology converts digital models into real physical products with remarkable accuracy. CNC machines such as milling machines, turning machines, and electric discharge machines (EDM) are commonly used. The cutting tools in these machines can follow data from the digital models, allowing for precise cuts and the creation of molds that meet exact specifications.
2. Laser Processing Technology
Laser processing offers a fast, efficient, and flexible way to manufacture molds. Laser cutting, marking, and welding techniques allow for intricate shapes to be formed with high precision, without damaging the surface of the workpiece.
Applications: Laser cutting and marking are used for processing metal plates, while laser welding is mainly used for mold repairs and the manufacturing of complex parts.
3. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
EDM is a technique that uses a moving metal wire (electrode) to discharge electrical sparks, removing material from the workpiece to shape it. This technique is highly effective for creating precision molds and parts, especially when dealing with hard materials like hardened steel and carbide.
Advantages: EDM is perfect for machining materials with high hardness and brittleness, providing an excellent finish and high precision.
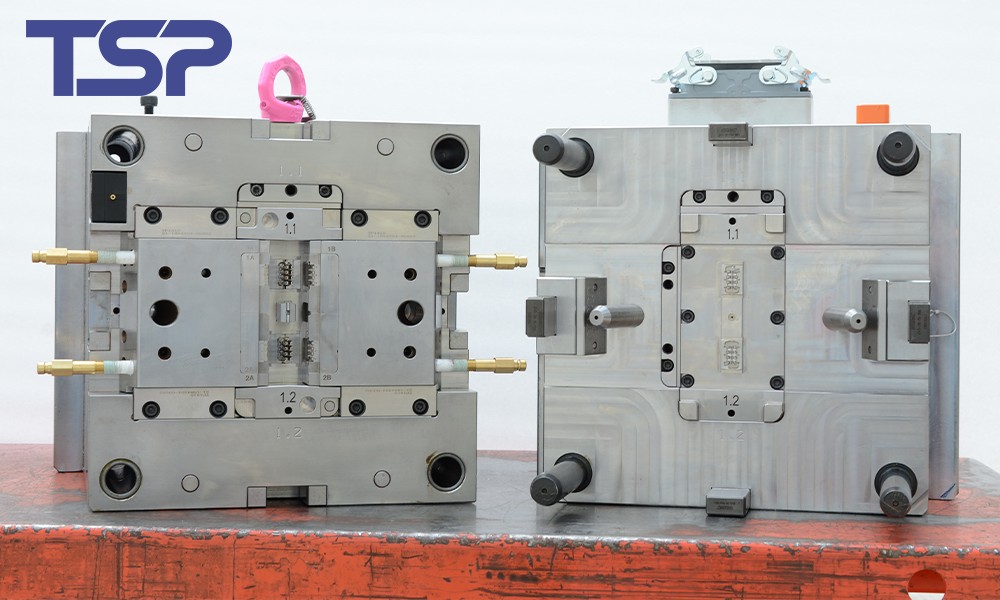

How to Choose the Right Mold Manufacturing Method
The selection of the right mold manufacturing technique depends on various factors, such as the material being used, the required precision, and the type of mold needed. The most commonly used methods are:
CNC Machining: Ideal for high-precision and repeatable parts.
Laser Processing: Best for intricate designs and quick production.
EDM: Suitable for hard materials and high-precision parts.
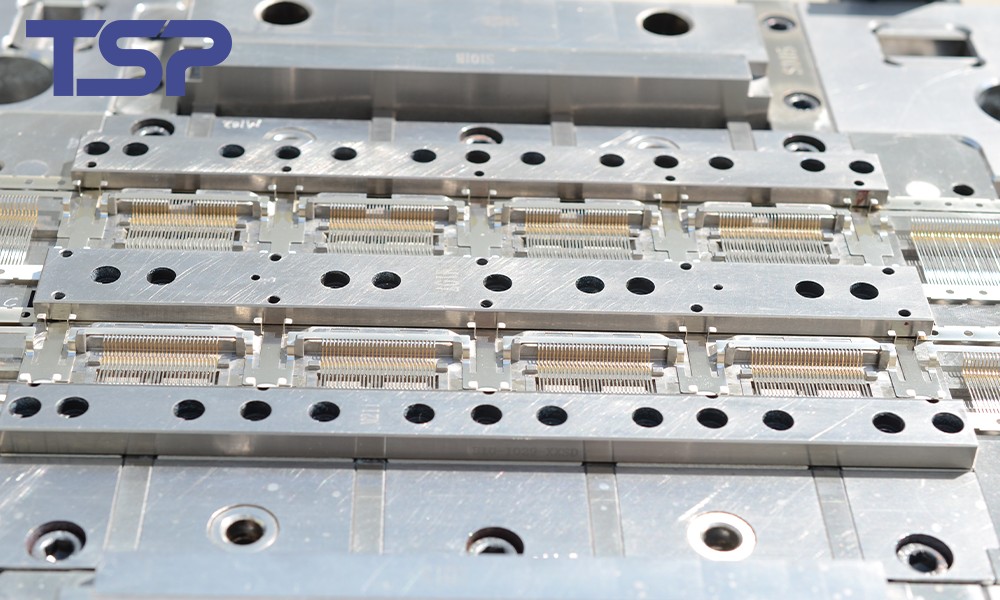

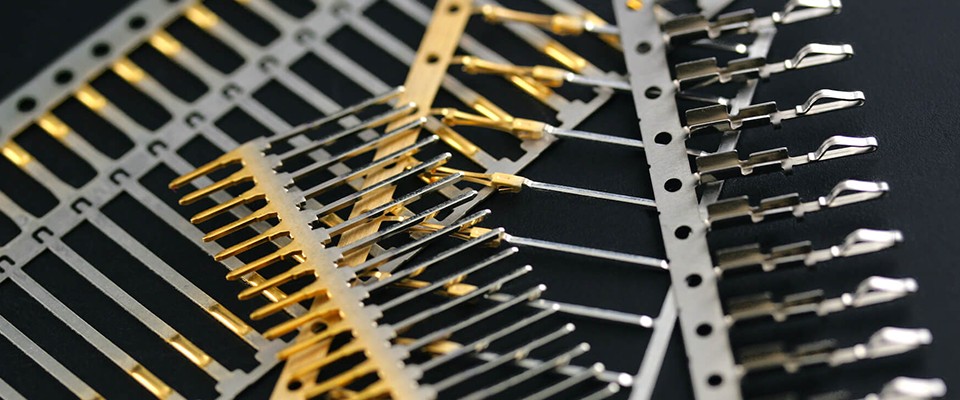
The Importance of Precision Injection Molds in Medical Devices
Precision molds are critical in the medical industry. They directly affect the quality and performance of the final medical product. By using accurate designs, high-quality materials, and advanced manufacturing techniques, companies can ensure the longevity, reliability, and safety of medical devices.
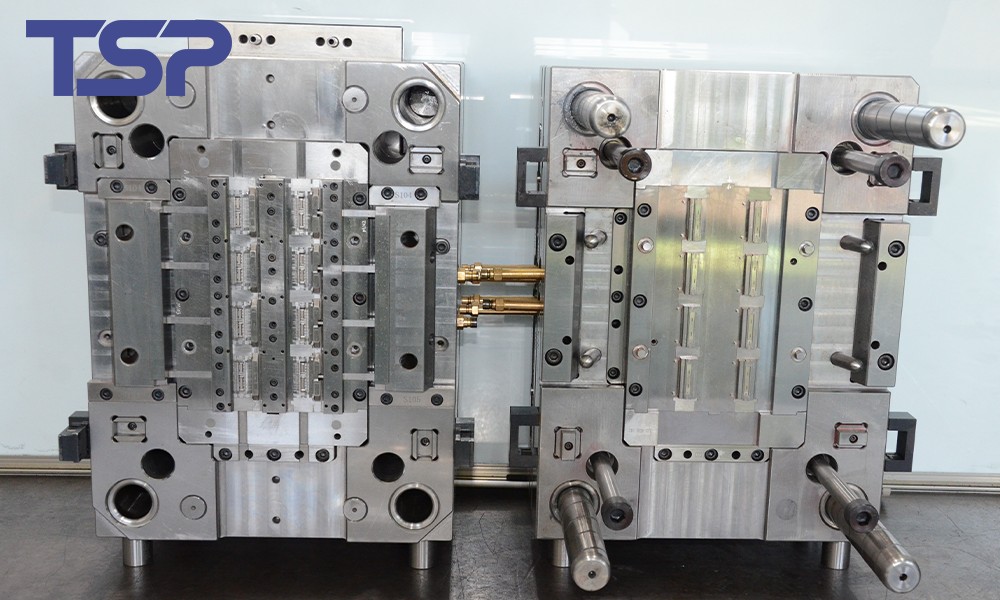

TSP — Why Choose Us
Over 26 years of mould & tooling mastery, delivering precision manufacturing at scale for global clients.
State‑of‑the‑art CNC, EDM, high‑speed milling, precision grinding and laser‑processing equipment — enabling mould tolerances down to ±0.01 mm with consistent repeatability.
50,000+ sqm manufacturing footprint spanning China (Shanghai & Anhui), Mexico, Morocco — offering reliable capacity and global supply chain support.
Broad industry coverage — from med‑tech, automotive, smart home to aerospace, e‑mobility and data‑center hardware — demonstrating versatility and cross‑sector expertise.
Commitment to quality & collaboration — every project backed by engineering know‑how, rigorous process control, and customer‑centric service from design to delivery.
TSP – Precision tooling, global capacity, trusted performance.
To read more: TSP Shanghai Achieves 1000KW Solar Power Milestone