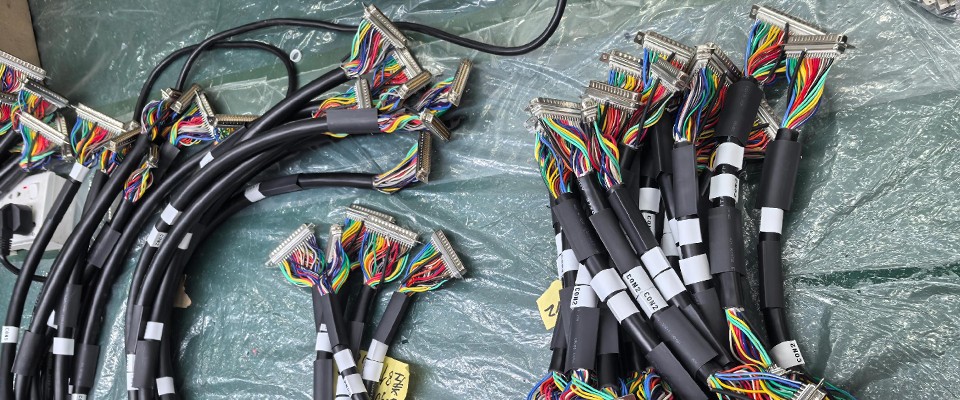
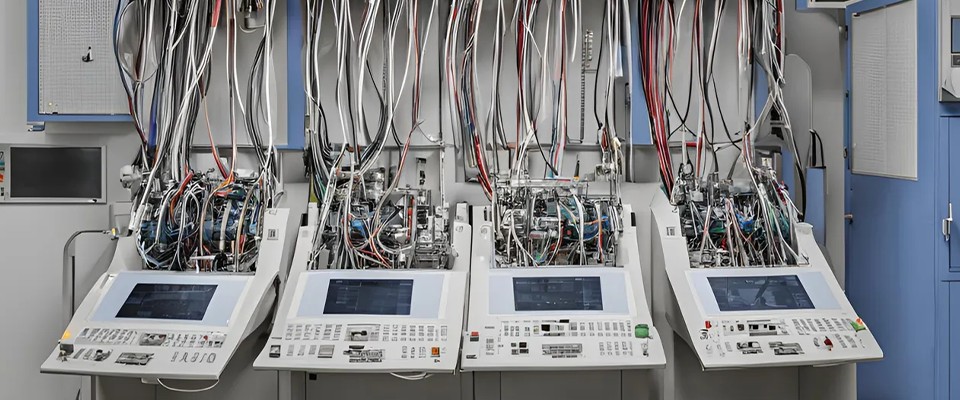
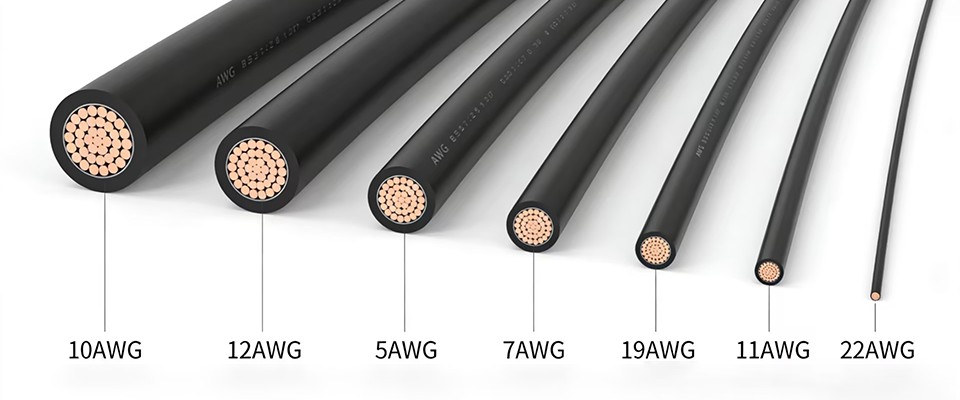
In modern industrial robotics and automated factories, the choice of cables plays a critical role in ensuring system reliability, operational efficiency, and safety. Industrial robots undergo continuous motion and repetitive bending, which places enormous mechanical stress on cables. Selecting cables with high flexibility, excellent bend resistance, and long drag chain lifetime is essential for maintaining optimal performance in manufacturing and automation environments.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of industrial robot cable selection, covering technical specifications, environmental considerations, cable types, and best practices. By understanding these factors, manufacturers and system integrators can make informed decisions that reduce downtime, improve productivity, and extend equipment lifespan.
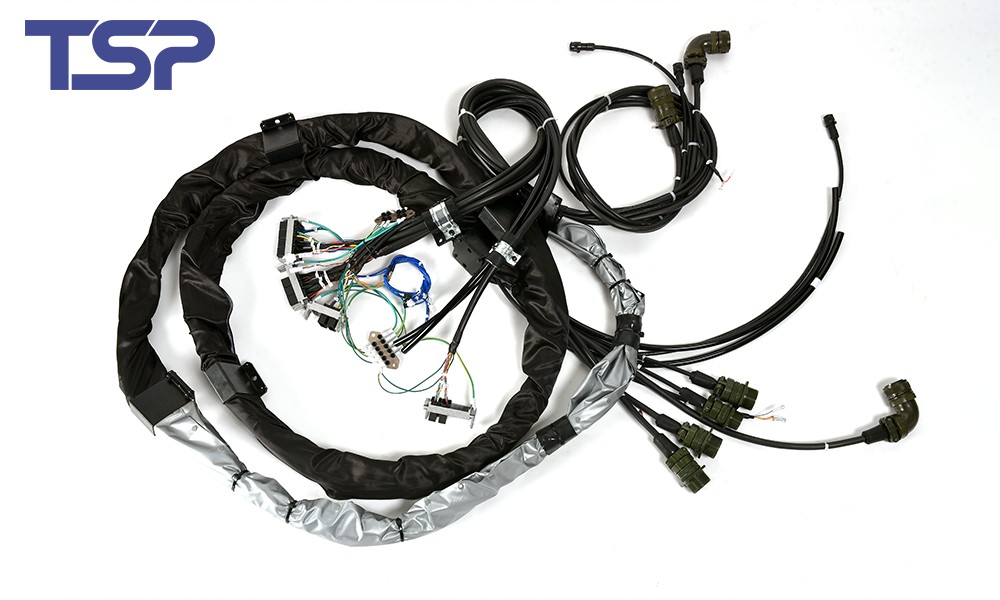

1. Key Performance Requirements for Industrial Robot Cables
Industrial robot cables must meet stringent mechanical, electrical, and environmental requirements. The most critical performance characteristics include:
1.1 High Flexibility
Robotic arms move along multiple axes at high speed. Cables must endure repeated bending and torsion while maintaining stable power and signal transmission. High-flexibility cables are typically constructed with fine-stranded conductors and flexible insulation materials such as PUR (Polyurethane) or TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer).

1.2 Drag Chain Lifetime
Industrial robots frequently operate in drag chains that guide and protect cables. Drag chain-rated cables are tested for friction resistance, torsional stress, and dynamic bending, ensuring reliable operation for the full lifecycle of the robot. Selecting cables that exceed expected drag chain lifetimes minimizes maintenance costs and avoids unexpected downtime.

2. Factors to Consider When Selecting Industrial Robot Cables
When choosing cables for industrial robots, several factors should be evaluated:
2.1 Mechanical Parameters
Motion range and axis speed
Twisting and bending cycles
Cable routing and length within drag chains
2.2 Electrical Parameters
Rated voltage and current capacity
Signal integrity for high-speed communication (Ethernet, CAN bus, servo feedback)
Shielding requirements to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI)
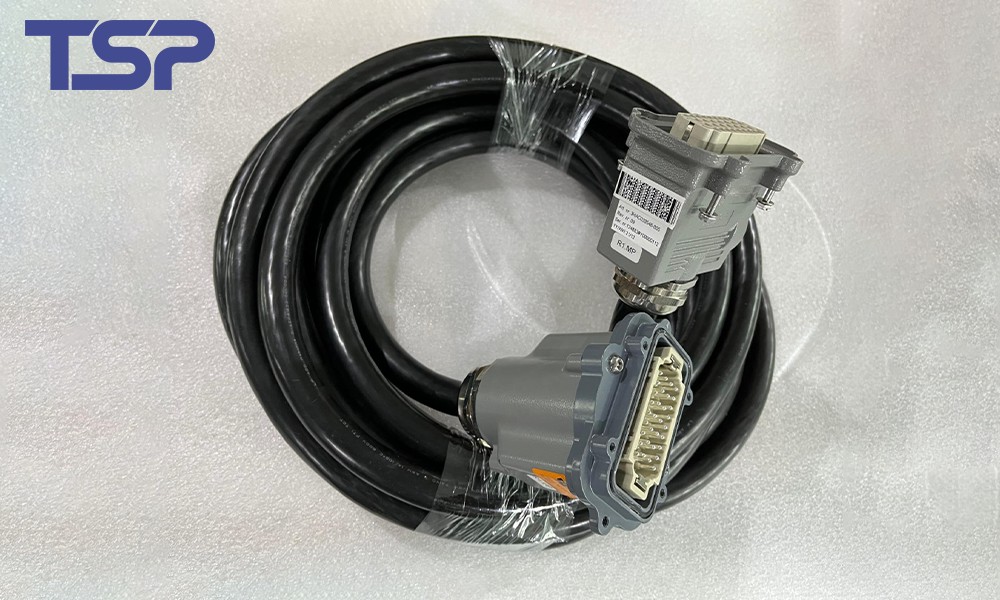

2.3 Environmental Conditions
Temperature range (low/high)
Resistance to oil, chemicals, water, and UV exposure
Flame retardant and halogen-free insulation for safety compliance
2.4 Installation Considerations
Drag chain vs. free routing
Space constraints and minimum bend radius
Maintenance and replacement accessibility

3. Types of Industrial Robot Cables
Understanding the types of cables used in robotics is essential for correct selection:
3.1 Servo Motor and Drive Cables
Connect servo drives to motors and ensure precise torque and speed control. High-quality insulation and flexible conductors maintain signal integrity during repeated motion.
3.2 Data and Bus Cables
Support industrial communication protocols, including Ethernet, CAN, and proprietary bus systems. Cables must provide low-loss transmission with robust shielding against electromagnetic interference.
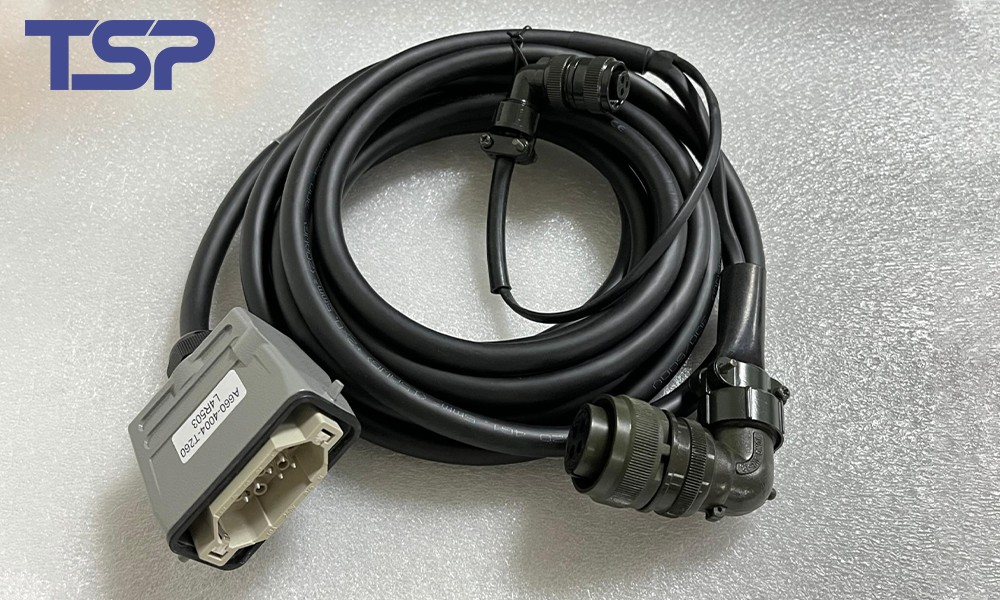

3.3 Power Cables
Deliver electrical power to end effectors, robotic arms, or actuators. They require high current capacity, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure.
3.4 Hybrid Cable Assemblies
Combine power, data, and signal conductors into a single cable assembly. Hybrid assemblies simplify installation, reduce space usage, and enhance reliability in complex robot systems.
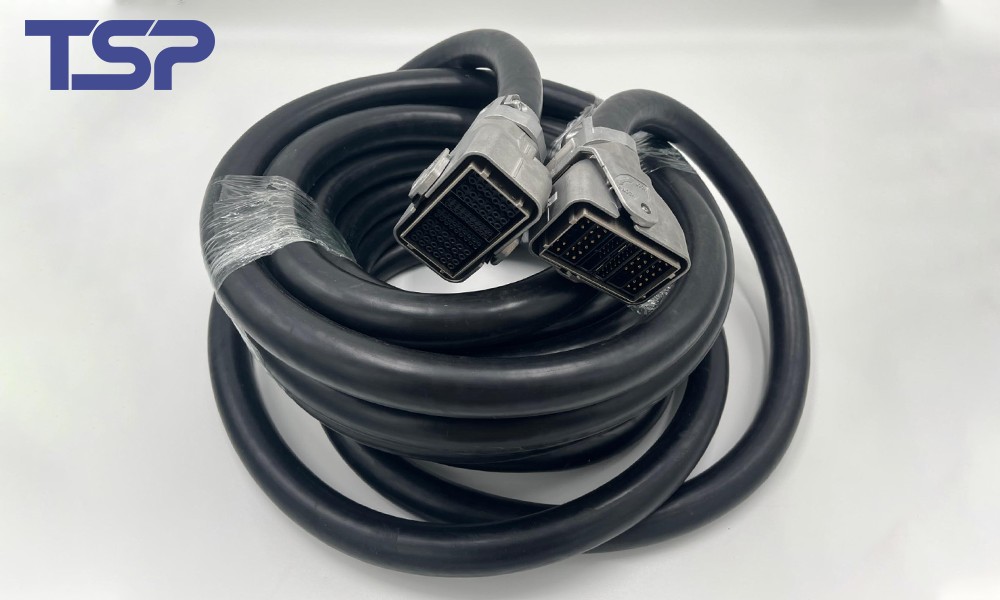

4. TSP Industrial Robot Cable Solutions
TSP specializes in high-precision cable assemblies and wiring solutions for industrial robots and automated factories. With global manufacturing facilities in China, Mexico, and Morocco, TSP serves clients across North America, Europe, and Asia. Key advantages include:
High Flexibility: Cables are tested for millions of bending cycles in dynamic motion applications.
Durable Materials: PUR and TPE insulation provide resistance to oil, chemicals, wear, and extreme temperatures.
Custom Cable Assemblies: Designed for leading industrial robot brands including ABB, KUKA, FANUC, and Yaskawa.
Comprehensive Service: From design and prototyping to full-scale production and assembly, TSP delivers turnkey solutions.

5. Practical Guidelines for Cable Selection
Selecting the right cable ensures optimal performance and minimizes maintenance costs:
Assess Application Requirements: Determine robot type, motion frequency, and environmental conditions.
Evaluate Mechanical Stress: Consider bend radius, torsion, and drag chain dynamics.
Ensure Electrical Performance: Verify voltage, current, and signal transmission requirements.
Consult Industry Experts: Partner with experienced manufacturers such as TSP for OEM and ODM solutions tailored to your robotic systems.
Plan for Maintenance: Use modular, easy-to-install assemblies to reduce downtime and simplify replacement.

6. Benefits of Proper Industrial Robot Cable Selection
Increased robot and factory equipment reliability
Extended cable and robot lifecycle
Reduced maintenance and replacement costs
Stable power and data transmission, improving operational efficiency
Compliance with safety and industry standards

To read more: TSP Shanghai Achieves 1000KW Solar Power Milestone