— Analyzing Growth in the Asia-Pacific and Latin America Markets and Practical Supply Chain Localization Strategies
I. Emerging Market Surge: Asia-Pacific and Latin America as New Growth Hubs for the Global Medical Injection Molding Market
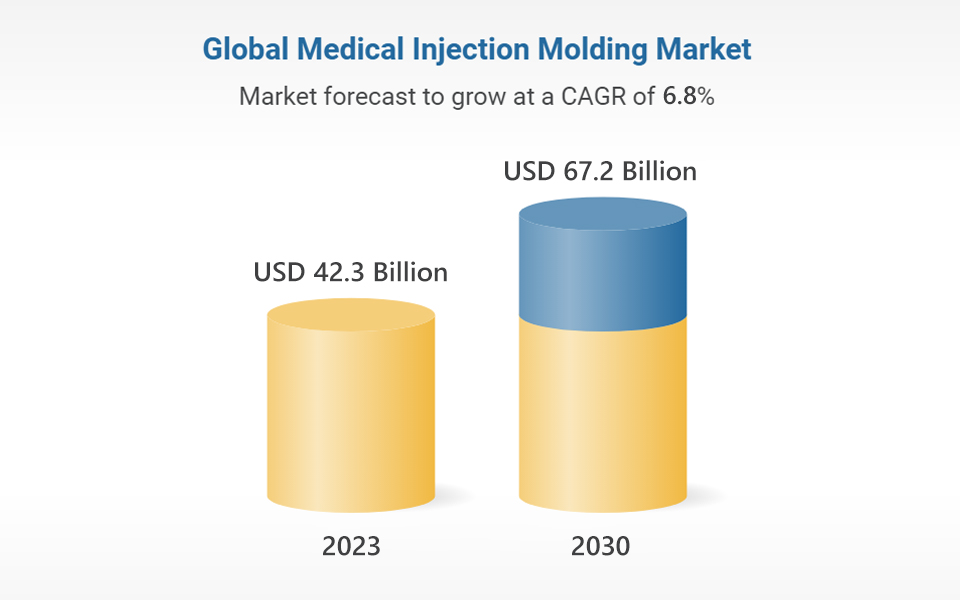
According to publicly available market research reports, the global medical injection molding market is expected to grow from USD 42.3 billion in 2023 to USD 67.2 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.8%. Of this growth, the Asia-Pacific and Latin American regions are projected to contribute over 50%, driven by key factors such as:
Aging Populations and Healthcare Infrastructure Upgrades:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the percentage of the population aged 65 and above is expected to increase from 9.3% in 2020 to 13.1% by 2030 (UN data), driving significant demand for disposable medical devices and diagnostic consumables.
Local Policy Incentives:
For example, India’s “Make in India” initiative has raised medical device import tariffs, boosting local manufacturing. Similarly, some Latin American countries have introduced tax incentives to attract foreign investment in local production, increasing demand for domestic manufacturing.
Supply Chain Cost Advantages:
Mexico, for instance, offers a cost advantage for medical injection molding, with production costs being 30%-40% lower than in the U.S., and its proximity to North America makes it an ideal location for “nearshoring” strategies by multinational corporations.
II. Supply Chain Localization: From "Globalization" to "Regionalization" — A Practical Strategy Guide
As the limitations of pure globalization become evident, an increasing number of medical device companies are shifting production to emerging markets, with 75% of global medical device firms planning to localize at least 30% of their production capacity within the next three years, according to a 2023 McKinsey survey. Here are key regional strategies for this shift:
1. Asia-Pacific: Clustered Industry Development
• India: With its advantage in low-cost labor and relatively inexpensive generic drug materials, the medical injection molding market in India is expected to grow at a rate of 12%. For example, Poly Medicure has reduced its infusion set molding costs by 20% through local mold development.
• Southeast Asia: Thailand and Malaysia, with their ISO 13485 certification clusters, have become hotspots for high-end injection molding orders. Penang, Malaysia, has evolved into a “medical silicon valley” housing 30 medical injection molding companies.
2. Latin America: Nearshoring “Quick Response Base”
• Mexico: In 2022, Mexico’s medical injection molding exports reached USD 4.7 billion, primarily serving the U.S. market. Companies like Nemera have been able to deliver respiratory mask prototypes within 48 hours by working with local mold manufacturers.
• Brazil: The Brazilian government’s “Health+5” program has invested USD 300 million to upgrade medical manufacturing equipment, attracting companies like Sumitomo and Siemens to establish high-precision injection molding production lines.
III. Key Challenges and Solutions for Successful Localization
While the prospects for medical injection molding in emerging markets are promising, companies face several challenges in implementing localization strategies:
1. Technological and Compliance Barriers
• Challenge: Only 30% of local mold manufacturers in India can consistently produce medical-grade parts with tolerances of ±0.01mm (according to data from the Indian Medical Device Association).
• Solution: Collaborating with local top-tier companies to form joint ventures and implementing standardized production management systems. For example, a German company established a technical center in Pune, India, to provide mold standardization training and management practices.
2. Supply Chain Fragmentation
• Challenge: In Latin America, resin materials are largely imported, which can lead to a 2-3 week delay compared to North American supply chains.
• Solution: Setting up regional raw material supply centers to reduce delays. For example, DuPont has established a modified plastics factory in Monterrey, Mexico, to serve clients within a 500 km radius.
3. Talent Gaps
• Challenge: Only 15% of workers in Vietnam have received specialized training in medical injection molding (according to the Vietnamese Ministry of Labor).
• Solution: Partnering with local vocational training institutes to offer customized courses. For instance, a major medical device company has established a “Medical Injection Molding Craftsmanship Class” in Indonesia, training 200 technicians annually.
IV. Case Studies: How Multinational Corporations Are Gaining the Upper Hand
Here are examples of multinational companies successfully localizing their operations in emerging markets:
Case 1: Medical Devices Company in India
A medical devices company acquired a local Indian company to leverage its low-cost mold development capabilities, reducing injection molding costs for blood glucose test strips by 18%. The company not only increased responsiveness to local market demands but also met regulatory certification requirements in India.
Case 2: Medical Devices Company in Mexico
A major medical devices company set up a “Mold Rapid Response Center” in Tijuana, Mexico, collaborating with local suppliers to shorten the injection molding cycle for CT scanner housings from 90 days to 45 days, boosting production capacity by 40%.
V. Future Trends: Shifting from "Cost-Driven" to "Technology + Localization" Dual-Drivers
By 2030, the medical injection molding market in emerging countries will experience two key trends:
Low-End Market:
Countries like India and Vietnam will focus on low-cost consumables (such as syringes and catheters), with profit margins around 8%-12%.
High-End Market:
Countries like Mexico and Malaysia, leveraging technology transfers from Western markets, will focus on high-end products such as minimally invasive surgical instruments and smart sensor housings, with profit margins ranging from 20%-25%.
Conclusion
The explosion of the medical injection molding market in emerging countries presents both opportunities and challenges. Companies relying solely on low-cost competition may fall into the “economies of scale” trap. To establish long-term competitive advantages, it is crucial to combine localization with technological innovations (such as smart molds and biodegradable materials). A critical question remains: Can your supply chain support regional demand fluctuations over the next five years?
Disclaimer: The data and trends mentioned in this article are sourced from publicly available research reports and studies, including those from Grand View Research (2023) and Frost & Sullivan, among others. Actual data may vary with market changes. Company names and examples are based on publicly available information or corporate financial reports and do not constitute an endorsement or recommendation.