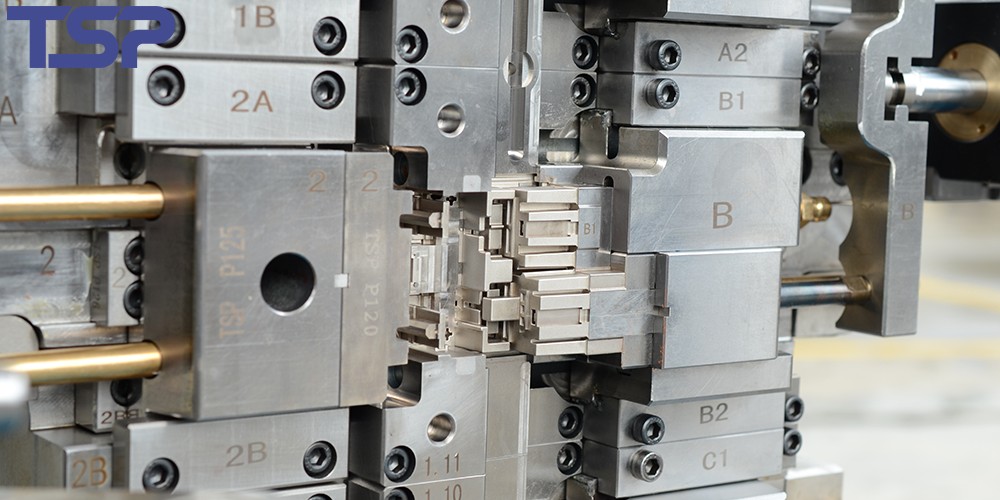
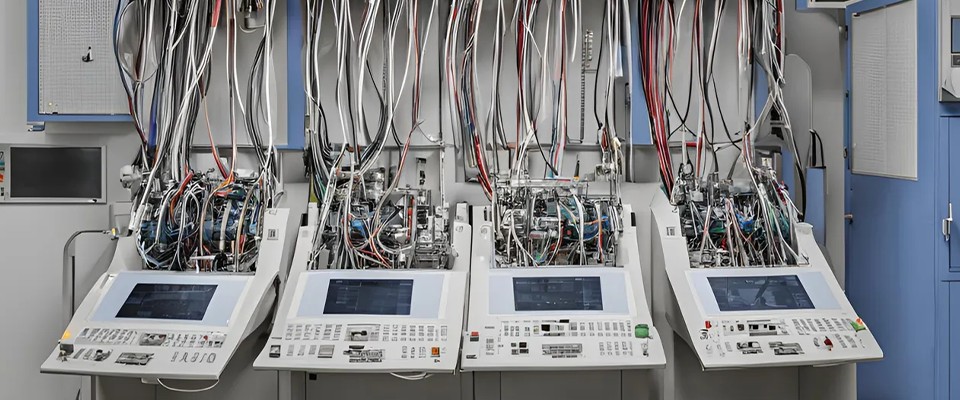
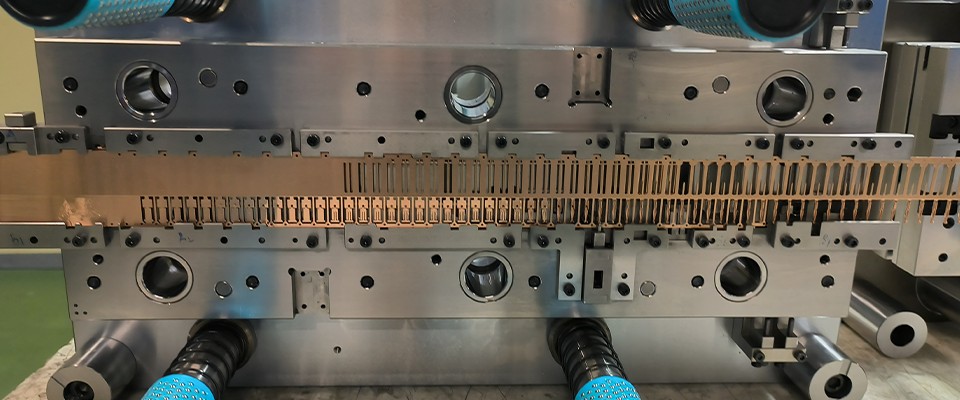
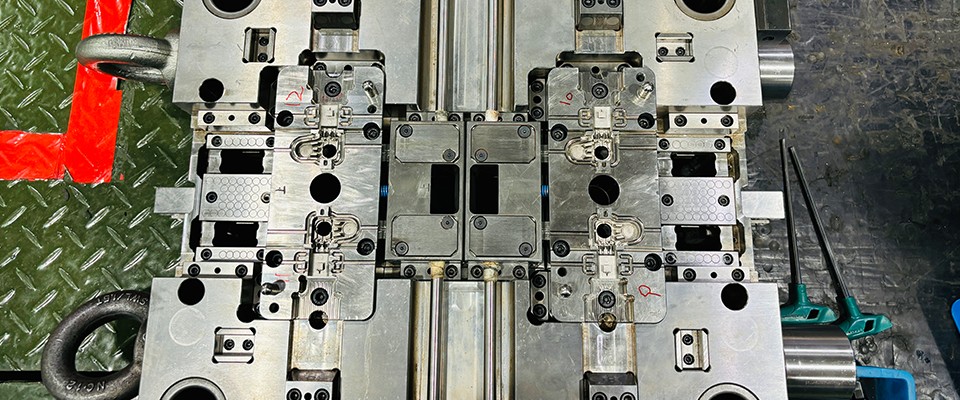
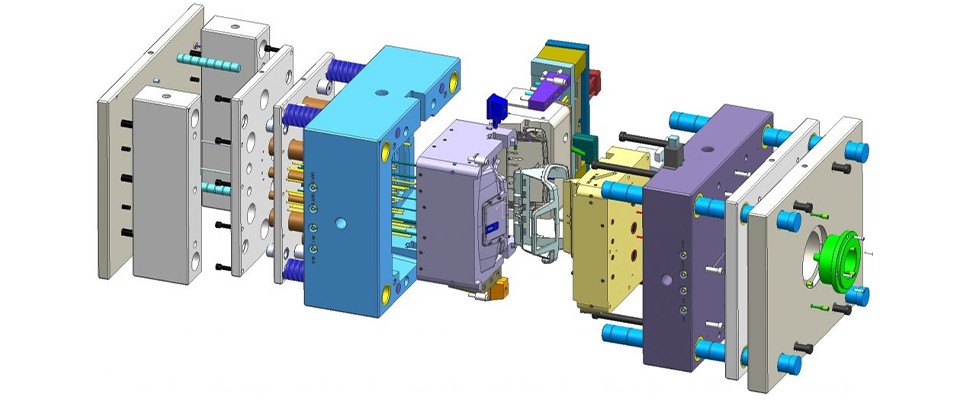
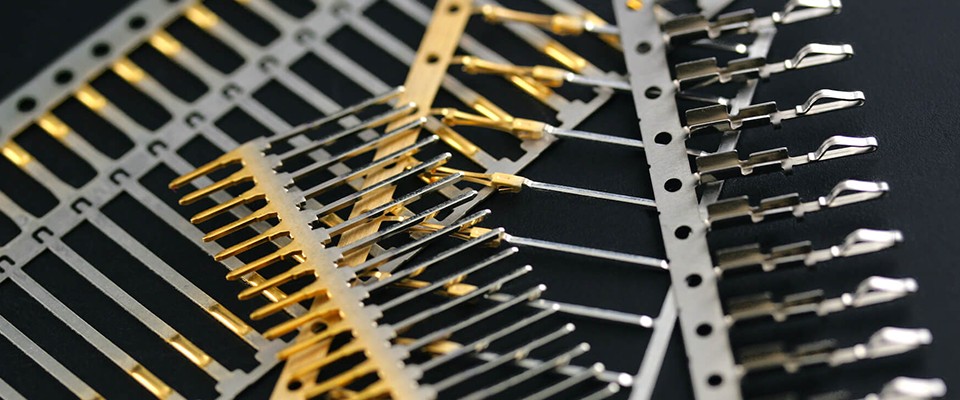
1. What is a Precision Mold?
Precision molds are critical tools in manufacturing that shape raw materials into high-precision, high-quality components. They meet stringent requirements for size, shape, and performance across industries such as automotive, electronics, medical, and industrial sectors.
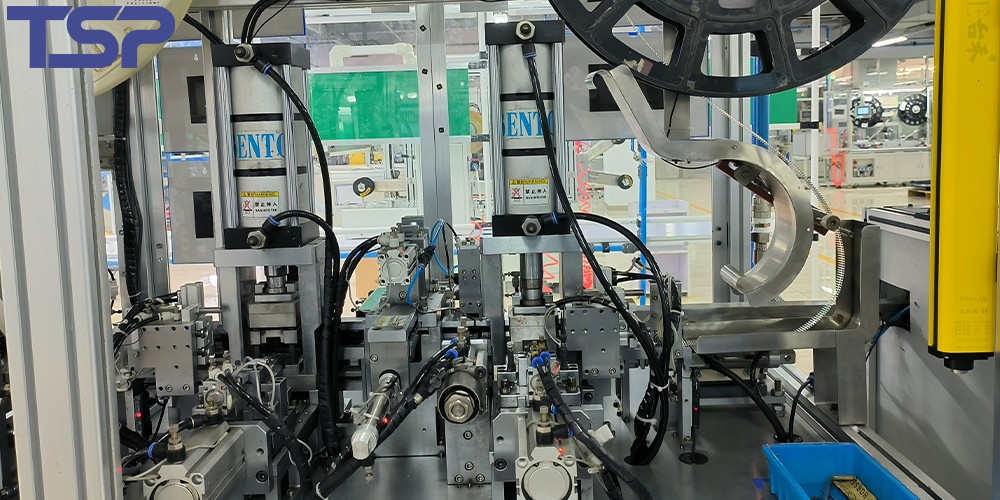

2. Detailed Classification of Precision Molds
2.1 Injection-Type Molds
Structure and Process
Injection molds and die casting molds fall into this category. These molds feature cavities, cores, gating systems, cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms. Molten material is injected at high pressure into the mold cavity, then cooled and solidified. Injection molds are used for thermoplastics, while die casting molds are for metal alloys.
Materials
Thermoplastics: ABS, PP, PC, PA, etc.
Metal alloys: Aluminum, zinc, magnesium
Typical Applications
Automotive dashboards and door panels
Electronic device housings (phones, laptops)
Medical device casings
Household appliance components
Advantages
Highly automated, suitable for mass production
High precision and intricate details
Fast cooling cycles
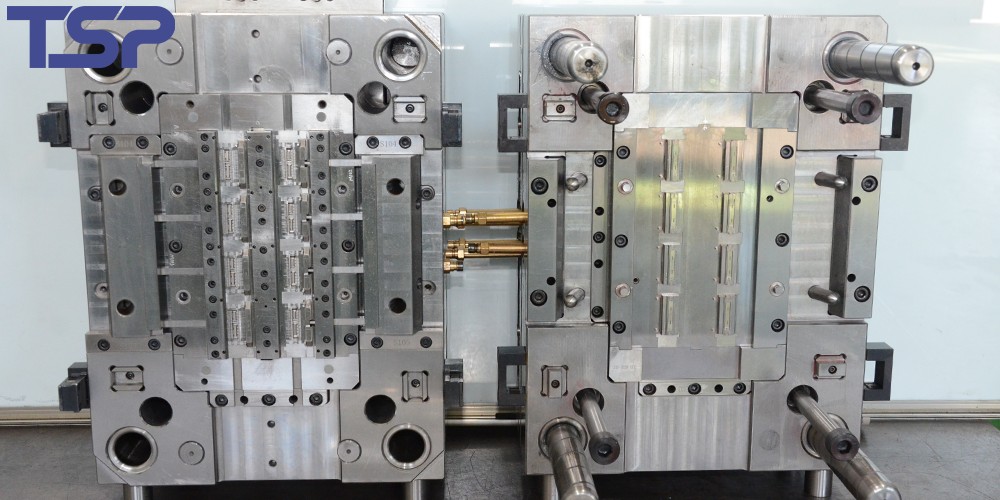
2.2 Compression-Type Molds
Structure and Process
Compression molds have simpler designs, typically upper and lower halves without gating systems. Thermosetting plastics or rubber materials are placed directly in the mold cavity, then heat and pressure are applied to cure the material. Powder metallurgy molds also belong here, compressing metal powders into parts.
Materials
Thermosetting plastics: DMC, BMC
Rubber materials: Silicone, natural, synthetic rubber
Metal powders: Iron-based, copper-based
Typical Applications
Electrical insulation housings
Automotive engine parts
Seals and vibration dampers
Mechanical gears and bearings
Advantages
Suitable for heat-resistant and high-strength parts
Lower mold manufacturing cost and easy maintenance
Can process difficult-to-melt and elastic materials
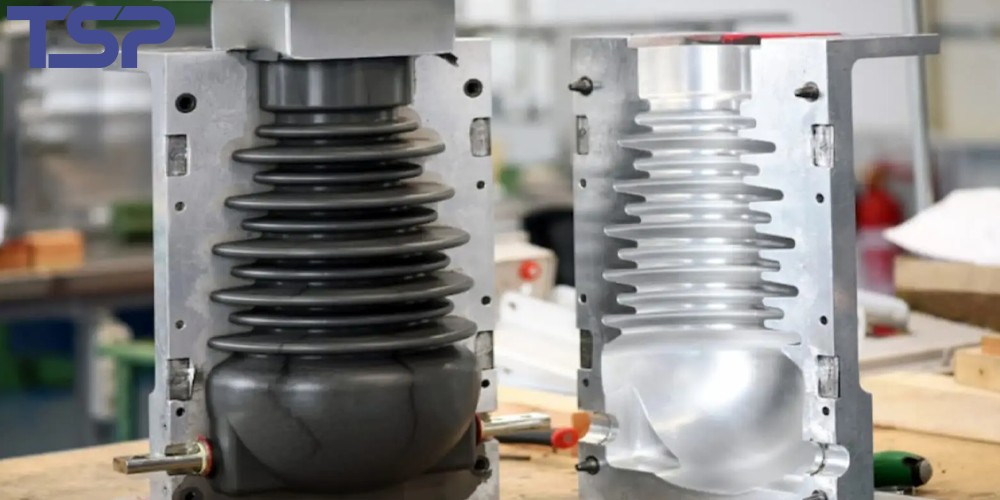

2.3. Sheet-Metal Dies
Structure and Process
These molds are used to stamp, deep draw, and bend metal sheets with presses. Components include upper die, lower die, guide posts, and ejector mechanisms, providing stable, efficient forming.
Materials
Various steel sheets (cold rolled, hot rolled, stainless steel)
Aluminum alloy sheets
Typical Applications
Automotive body panels
Battery connectors
Appliance metal housings
Industrial equipment enclosures
Advantages
High production efficiency, suitable for large volumes
Precise and repeatable dimensions
Mature, stable processes
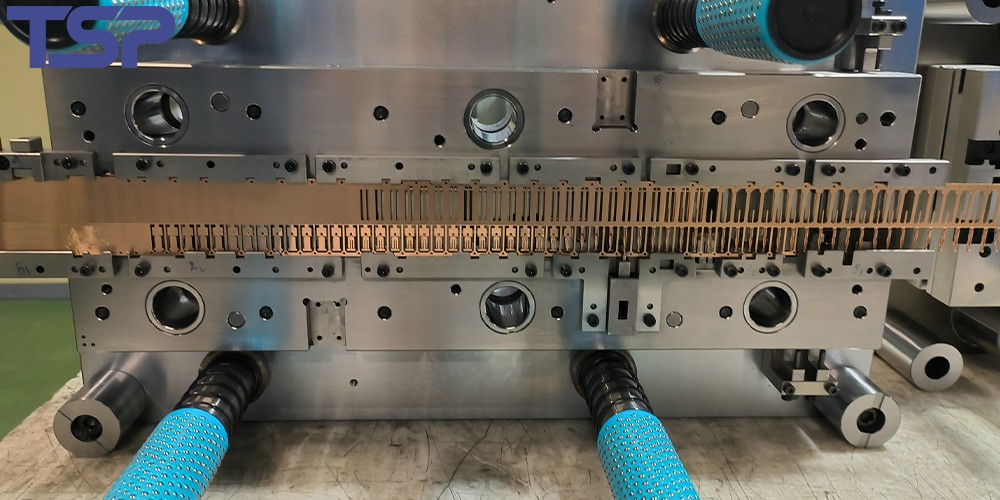
2.4. Specialty Molds
Structure and Process
Specialty molds are custom-designed for unique materials and forming methods, including:
Wire drawing dies: For thinning metal wires via carbide openings
Optical molds: High-precision molds for optical plastic or glass parts with ultra-smooth surfaces
Glass molds: High-temperature resistant molds for glass bottles and containers
Spinning molds: For rotational forming of thin-wall metal parts
Materials
Copper, aluminum, steel wire
Optical plastics and glass
Metal sheets
Typical Applications
Wire and cable manufacturing
Optical lenses and lighting
Glass bottles and containers
Aerospace and pressure vessel parts
Advantages
Customized for special requirements
Ensures high precision and functionality
Meets high-value industry standards

3. Summary Comparison Table
| Category | Materials | Forming Process | Typical Applications | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection-Type Molds | Thermoplastics, metal alloys | High-pressure injection and cooling | Automotive electronics, medical, appliances | High precision, high efficiency, mass production |
| Compression-Type Molds | Thermosetting plastics, rubber, powders | Heat and pressure curing | Electrical parts, automotive, seals | Heat resistance, high strength, low cost |
| Sheet-Metal Dies | Various metal sheets | Stamping, deep drawing, bending | Auto body, battery parts, industrial equipment | High throughput, mature process |
| Specialty Molds | Wire, optical plastics, glass | Wire drawing, optical forming, spinning | Optics, cables, glass products, aerospace | Customization, high precision |

4. Conclusion
Choosing the right type of precision mold is foundational to smooth manufacturing and quality assurance. Understanding mold structures and applications enables manufacturers to optimize processes and enhance competitiveness. We offer comprehensive mold design and manufacturing services to help clients achieve high quality and efficiency.

To read more: TSP Shanghai Achieves 1000KW Solar Power Milestone