Choosing the correct wire gauge for your wiring harness is a critical step in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical systems. Whether you’re designing for automotive applications, consumer electronics, or industrial machinery, the right wire size will directly impact current flow, heat dissipation, and overall system reliability. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key factors involved in selecting the perfect wire gauge for your custom wiring harness, and why getting it right is so crucial.

What is Wire Gauge?
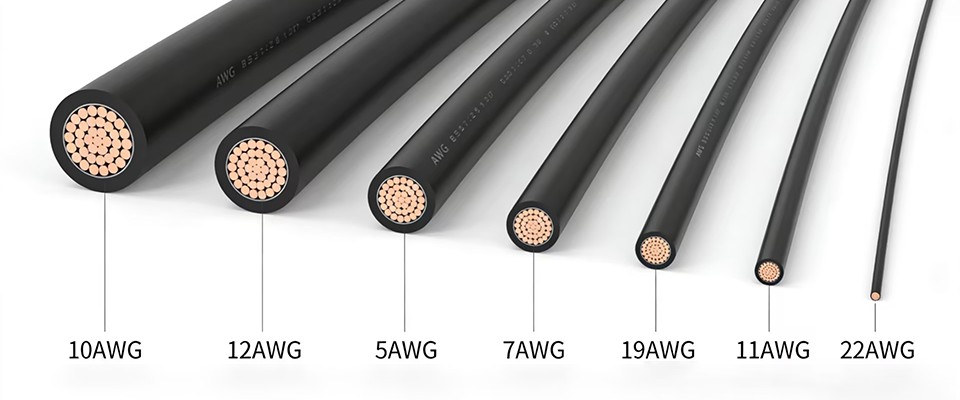
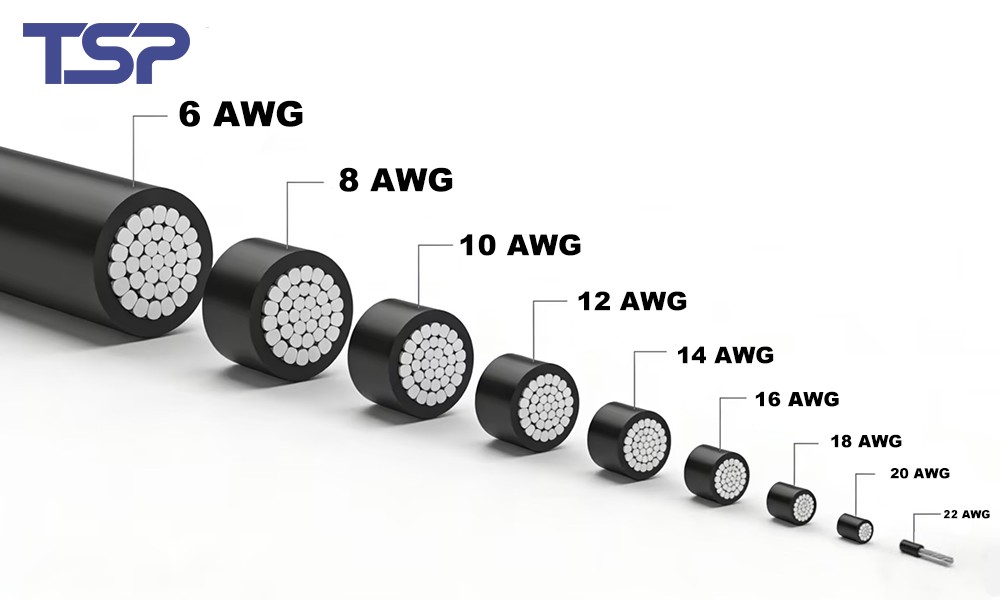
The wire gauge refers to the thickness of a wire and is typically measured in AWG (American Wire Gauge) in the U.S. The wire gauge directly correlates to the wire’s current-carrying capacity. In general, thicker wires (lower AWG numbers) can carry more current than thinner wires (higher AWG numbers).
Understanding AWG (American Wire Gauge)
AWG is a standardized system that defines wire thickness. The scale ranges from 00 (the thickest) to 40 (the thinnest). As the gauge number increases, the wire diameter decreases. For instance:
12 AWG wire is thicker than 16 AWG wire, meaning it can carry more current.
10 AWG is suitable for high-current applications like power distribution, while 20 AWG is used in low-current applications such as signal wiring.

Why Choosing the Correct Wire Gauge Matters
Selecting the right wire size ensures optimal current flow, reduces heat buildup, and minimizes energy loss in your wiring harness. Choosing a wire that’s too thin can lead to overheating, voltage drops, or even fire hazards, while selecting a wire that’s too thick can increase the cost and complexity of the harness.
1. Prevents Overheating
Incorrectly sized wires can overheat when carrying more current than their rated capacity, potentially causing insulation failure or short circuits. The proper wire gauge ensures safe heat dissipation, preventing damage to the wire and other components.
2. Avoids Voltage Drops
A wire that’s too thin increases the resistance, leading to voltage drops over long distances. This can cause performance issues, especially in sensitive devices or systems.
3. Maximizes Current Capacity
Thicker wires have a lower resistance, allowing them to handle higher currents without excessive heat generation or performance loss.

Factors to Consider When Choosing the Correct Wire Gauge
When selecting the appropriate wire gauge, several factors must be taken into account. Let’s break down the key considerations:
1. Current Capacity (Ampacity)
One of the most important factors is the ampacity of the wire, which refers to the maximum current the wire can safely carry. The ampacity depends on the wire gauge and the insulation material. You can refer to industry-standard wire gauge charts to determine the recommended wire size based on your application’s current requirements.
Example:
15 amps: 14 AWG
20 amps: 12 AWG
30 amps: 10 AWG
2. Application Type
Different applications require different considerations:
Automotive Wiring: Automotive systems typically use 12 AWG to 16 AWG wires depending on the load.
Industrial Wiring: For higher loads or heavy-duty applications, wires from 8 AWG to 10 AWG are often used.
Consumer Electronics: These require smaller gauges, often 20 AWG or 22 AWG, for signal transmission or low-power connections.
3. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of the wire is another essential factor. Ensure that the wire insulation is rated for the maximum voltage of the system. For example, automotive wires are typically rated for 12V, while industrial wiring might require higher ratings like 600V or 1000V.
4. Temperature Range
Different environments require different temperature-resistant wires. For high-temperature environments, such as industrial or automotive wiring, high-temperature wire insulation such as Teflon or silicone rubber should be used.
5. Wire Insulation
The type of insulation used in the wire affects both its durability and heat resistance. For example, PVC insulation is ideal for general-purpose applications, while Teflon insulation is used in high-temperature or high-performance environments.
Wire Gauge Chart: Common Sizes and Their Uses
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Max Amps (for copper wire) | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|
| 10 AWG | 30 A | High-power circuits, electric motors |
| 12 AWG | 20 A | Automotive wiring, general power applications |
| 14 AWG | 15 A | Household appliances, small devices |
| 16 AWG | 13 A | Low power applications, lighting |
| 18 AWG | 10 A | Small appliances, low-voltage circuits |
| 20 AWG | 7 A | Signal transmission, low current |
| 22 AWG | 5 A | Small signal circuits, sensors |

How to Choose the Correct Wire Gauge for Your Wiring Harness
Step 1: Calculate the Current
Determine the maximum current that will flow through the wire based on the load and voltage requirements of your system. This will help you select the correct wire size.
Step 2: Refer to a Wire Gauge Chart
Use a reliable wire gauge chart to match the required current with the corresponding wire size. Be sure to consider the wire’s ampacity to prevent overheating and ensure safety.
Step 3: Factor in Environmental Conditions
Consider the operating temperature, moisture levels, and other environmental factors. Choose wire insulation that is rated for your specific conditions (e.g., high heat, outdoor exposure).
Step 4: Select the Appropriate Insulation
Based on your application, select a wire with the appropriate insulation. For instance, PVC for general use, Teflon for high-temperature environments, and rubber for flexibility and durability.
Step 5: Ensure Compatibility
Ensure that the wire gauge, insulation, and materials are compatible with the connectors and other components in your wiring harness. The wire should easily fit into the connectors and be able to withstand any mechanical stress during operation.

Choosing the right wire gauge for your wiring harness is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of your electrical system. By considering factors such as current capacity, environmental conditions, voltage rating, and temperature resistance, you can select the perfect wire gauge for your application. Always refer to reliable wire gauge charts and factor in all the specifics of your project to ensure optimal performance.
By following these steps and selecting the appropriate wire gauge, you can ensure safety, efficiency, and longevity in your wiring harnesses, whether you are designing for automotive, industrial, or consumer electronics applications.